Technical Data - Gearhead

1. Definition of Gearhead
It is a speed converter using gears and an
instrumental device to reduce the rpm of motor into the required rpm and
get a bigger torque.
2. Features of DKM Gearheads
Small type having a big transfer capability
Good durability
Wide range of gear ratio
Good durability
Wide range of gear ratio
3. The Kind of DKM Gearhead
⑴ According to Frame Size
Frame Size □60mm Gearhead
Frame Size □70mm Gearhead
Frame Size □80mm Gearhead
Frame Size □90mm Gearhead
Frame Size □70mm Gearhead
Frame Size □80mm Gearhead
Frame Size □90mm Gearhead
⑵ According to Direction of Output Shaft of Gearhead
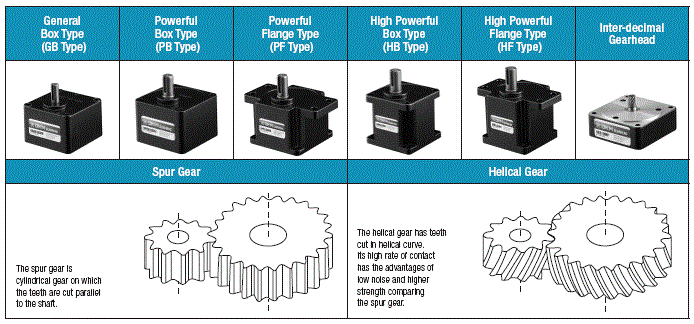
1) Parallel Gearhead
Parallel Gearhead is the most common type in small geared motor.
DKM employs spur type and helical type.
Especially the helical gear is employed for the low-noise and high-strength performance.
Regarding noise the important part in gear is the contacting point with motor shaft which rotating rapidly. DKM employed helical gear which cut high precisely in that point and realized low-noise performance.
DKM employs spur type and helical type.
Especially the helical gear is employed for the low-noise and high-strength performance.
Regarding noise the important part in gear is the contacting point with motor shaft which rotating rapidly. DKM employed helical gear which cut high precisely in that point and realized low-noise performance.
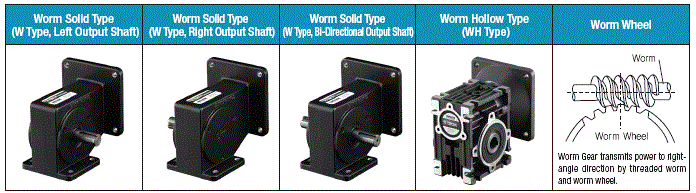
2) Worm Gearhead
Worm Gearhead has the advantage of using the
limited space with high efficiency and realizes the cost saving effect
by the reduction of using power transmission part like coupling.
DKM has worm solid type (for up to 120W) and worm hollow type (for 60W-200W).
DKM has worm solid type (for up to 120W) and worm hollow type (for 60W-200W).
4. The Efficiency of Gearhead
1) The Efficiency of Parallel Gearhead
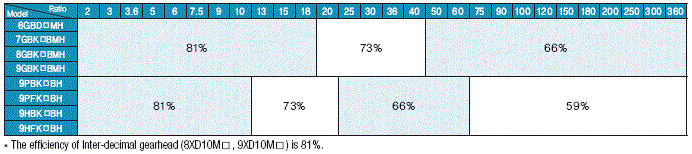
2) The Efficiency of Worm Gearhead

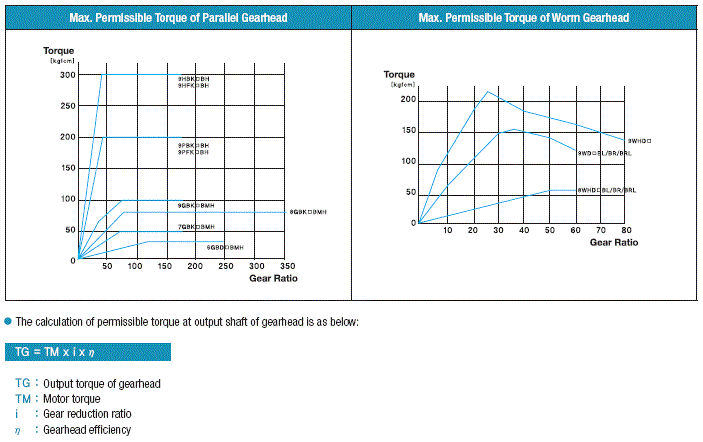
5. Maximum Permissible Torque
The output torque of gearhead is in proportion to the gear ratio.
But there is limit in the size of load which can be applied to the gearhead in specific gear ratio depending on gear construction and materials etc. affecting the gearhead mechanical strength.
This torque is called the maximum permissible torque.
The maximum permissible torques of typical gearheads are shown in the figure.
But there is limit in the size of load which can be applied to the gearhead in specific gear ratio depending on gear construction and materials etc. affecting the gearhead mechanical strength.
This torque is called the maximum permissible torque.
The maximum permissible torques of typical gearheads are shown in the figure.
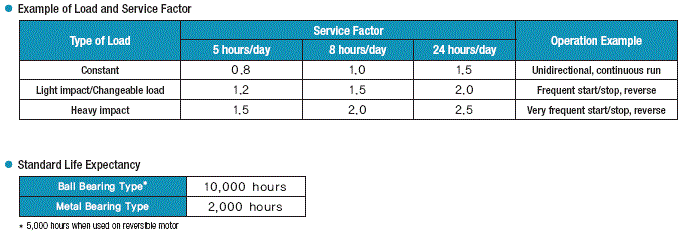
6. Gearhead Life Expectancy and Service Factor
Life expectancy of gearhead varies depending on
load fluctuation and is determined by the 'service factor' based on its
load. Service factor is a coefficient which is used to estimate the
service life of the gearhead. This value is generally derived from
experience and based on type of the load and operating conditions. The
standard life can be expected when the product is operated at service
factor 1.0. The life of a component during particular application is
estimated by dividing the standard life expectancy by the service
factor.
For example, if the motor is operating with an ordinary load for 8 continuous hours a day, the service factor is 1.0. Thus, if the operation continues within the permissible torque for the gearhead and within the range of prescribed temperature (letting the gearhead case temperature stay below 50℃), the life expectancy of the gearhead is 10,000 hours for the ball bearing type and 2,000 hours for the metal type. However, if a ball bearing type of gearhead is operating for 24 hours a day, the service factor becomes 1.5 so that the life expectancy decreases to 1/1.5. Therefore the service factor should be taken into acoount to select such a motor and a gearhead which have biggest permissible torque.
For example, if the motor is operating with an ordinary load for 8 continuous hours a day, the service factor is 1.0. Thus, if the operation continues within the permissible torque for the gearhead and within the range of prescribed temperature (letting the gearhead case temperature stay below 50℃), the life expectancy of the gearhead is 10,000 hours for the ball bearing type and 2,000 hours for the metal type. However, if a ball bearing type of gearhead is operating for 24 hours a day, the service factor becomes 1.5 so that the life expectancy decreases to 1/1.5. Therefore the service factor should be taken into acoount to select such a motor and a gearhead which have biggest permissible torque.
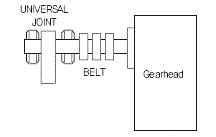
7. Overhung Load and Thrust Load
1) The
overhung load is defined as a load applied to the output shaft in the
right-angle direction. This load is generated when the gearhead is
coupled to the machine using a chain, belt, etc., but not when the
gearhead is directly connected to the coupling. The thrust load is
defined as a load applied to the output shaft in the axial direction.
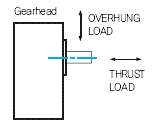
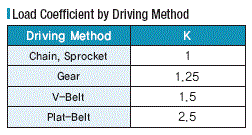
2) Since the overhung load exerts a load directly on the bearing, it affects the life span of the gearhead.
The overhung load can be calculated from the following equation.
The overhung load can be calculated from the following equation.

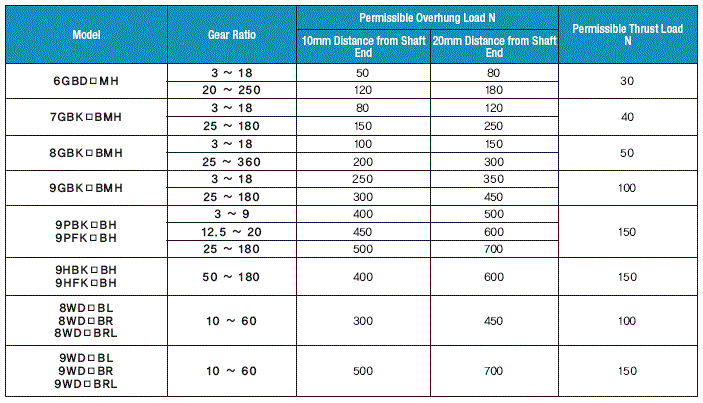
3)
If the motor operates with the calculated overhung load exceeds the
maximum allowable value in
below table, the output shaft may bend and the fatigue deformation may
occur due to the repeated load. So consider it and take care in sizing.
4)
In the case of that calculated overhung load value exceeds above
allowable value, please set up the structure of the motor as below to
withstand the overhung load.
5)
Also, if a load should be directly imposed on the output shaft, please
place the load as near to the gearhead as possible to avoid the
one-sided load.
6) In the case of that a helical gear or a worm gear is employed as an output delivery mechanism,
make sure not to exceed both the overhung load and the thrust load simultaneously.
8. Backlash Noise of Gearhead
1) Operating Noise of Gearhead
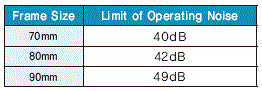
The backlash noise can be indicated by operating noise value.
DKM Gearhead’s operating noise is like below.
DKM Gearhead’s operating noise is like below.
< Reference>
i) Operating noise value is the value measured beside Gearhead with 1m distance.
ii) dB (decibel) is a unit of measurement which is used to indicate how loud a sound is.
iii) Level of operating noise (Ref. value)
20dB --- The sound of a leaf is shaking
30dB --- The sound in suburb of city in night time
40dB --- The sound in a silent park
50dB --- The sound in a silent office
ii) dB (decibel) is a unit of measurement which is used to indicate how loud a sound is.
iii) Level of operating noise (Ref. value)
20dB --- The sound of a leaf is shaking
30dB --- The sound in suburb of city in night time
40dB --- The sound in a silent park
50dB --- The sound in a silent office
2) The check point of Gearhead Noise
(1) Noise in no load
The backlash noise depends on the situation of load. For example, in case of no load rotation, gear could pop and crash between them therefore there could be little vibration and it could cause noise. This noise can be restrained and controlled by carrying some friction load.
The backlash noise depends on the situation of load. For example, in case of no load rotation, gear could pop and crash between them therefore there could be little vibration and it could cause noise. This noise can be restrained and controlled by carrying some friction load.
(2) Noise in Mounting with Load
When mounting is not good in mounting plate, there could be some noise by vibration caused from eccentric force. In this case, please check the mounting situation.
When mounting is not good in mounting plate, there could be some noise by vibration caused from eccentric force. In this case, please check the mounting situation.
(3) Noise of Damaged Gear
In assembly gearhead and motor, users have to turn the gearhead slowly according to the shape of pinion. Otherwise gear could get damaged. And by over load gear could get damaged. As a result there may some abnormal noise in gearhead. So please handle gearhead with special care in assembly.
In assembly gearhead and motor, users have to turn the gearhead slowly according to the shape of pinion. Otherwise gear could get damaged. And by over load gear could get damaged. As a result there may some abnormal noise in gearhead. So please handle gearhead with special care in assembly.
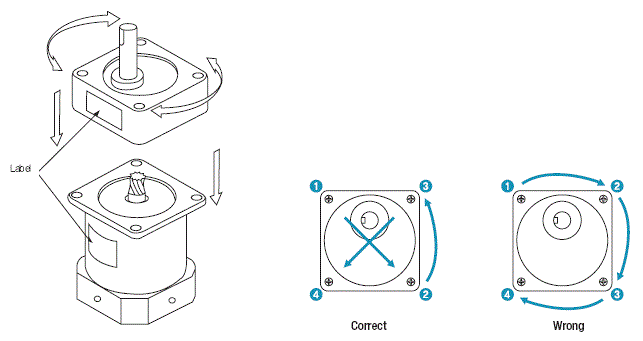
9. Assembly Method of Motor and Gearhead
To assemble the motor and the gearhead, adjust the
assembling faces together in such a way as shown in below figure and
turn slowly to complete the assembly.
When doing the assembly, special care should be taken neither to exert
excessive force on the motor shaft nor to hit inside of the gearhead.
Otherwise, the gear will get damaged, resulting in a abnormal noise and a
shortened lifetime of the motor.
Use the provided mounting screws for set mounting of gearhead and motor, and tighten the screws correctly. Be sure there is no-gab between motor flange, gearhead surface and the mounting surface.
Use the provided mounting screws for set mounting of gearhead and motor, and tighten the screws correctly. Be sure there is no-gab between motor flange, gearhead surface and the mounting surface.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar